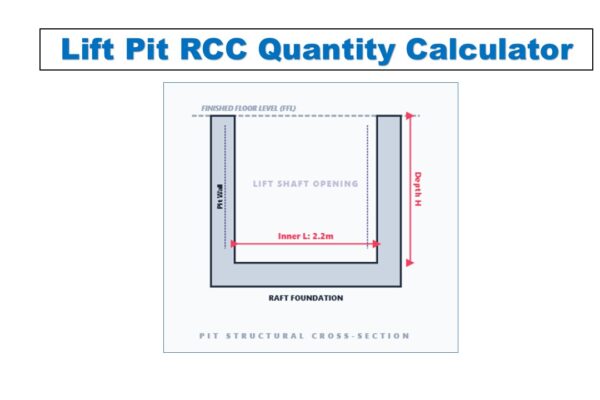
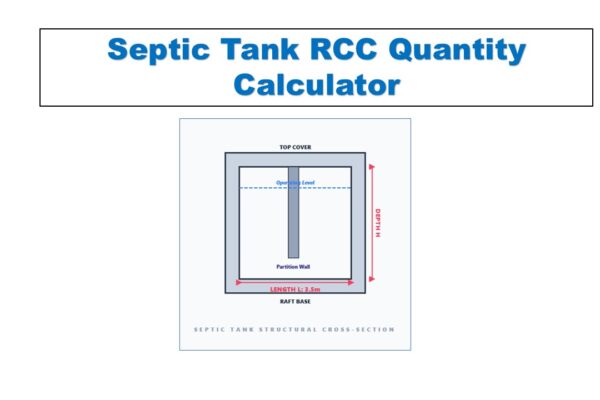
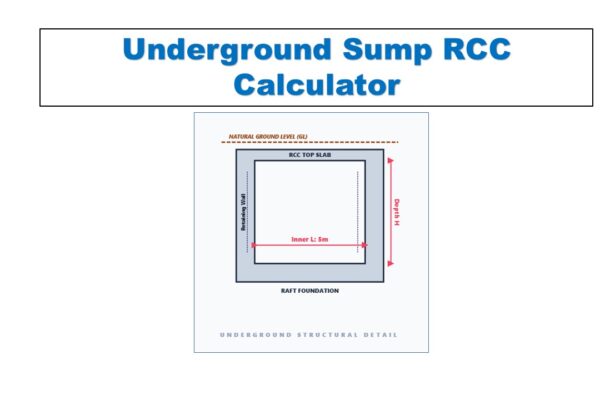
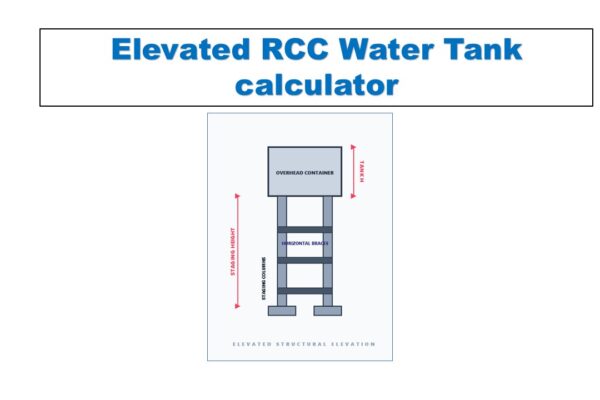
Monthly Progress Report (MPR) Tool | 12 Pillars of Project Management
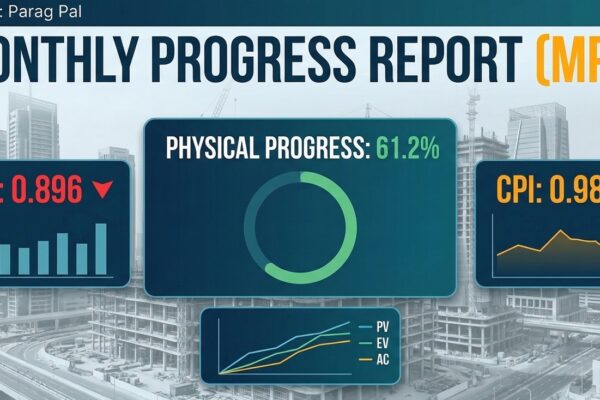
Introduction Monthly progress reporting for any project is important during project life cycle. It define the status of work done since inception and also define what is the current status of a project with respect to time and cost. Monthly progress reporting tool help project manager to generate the comprehensive report in limited time by…