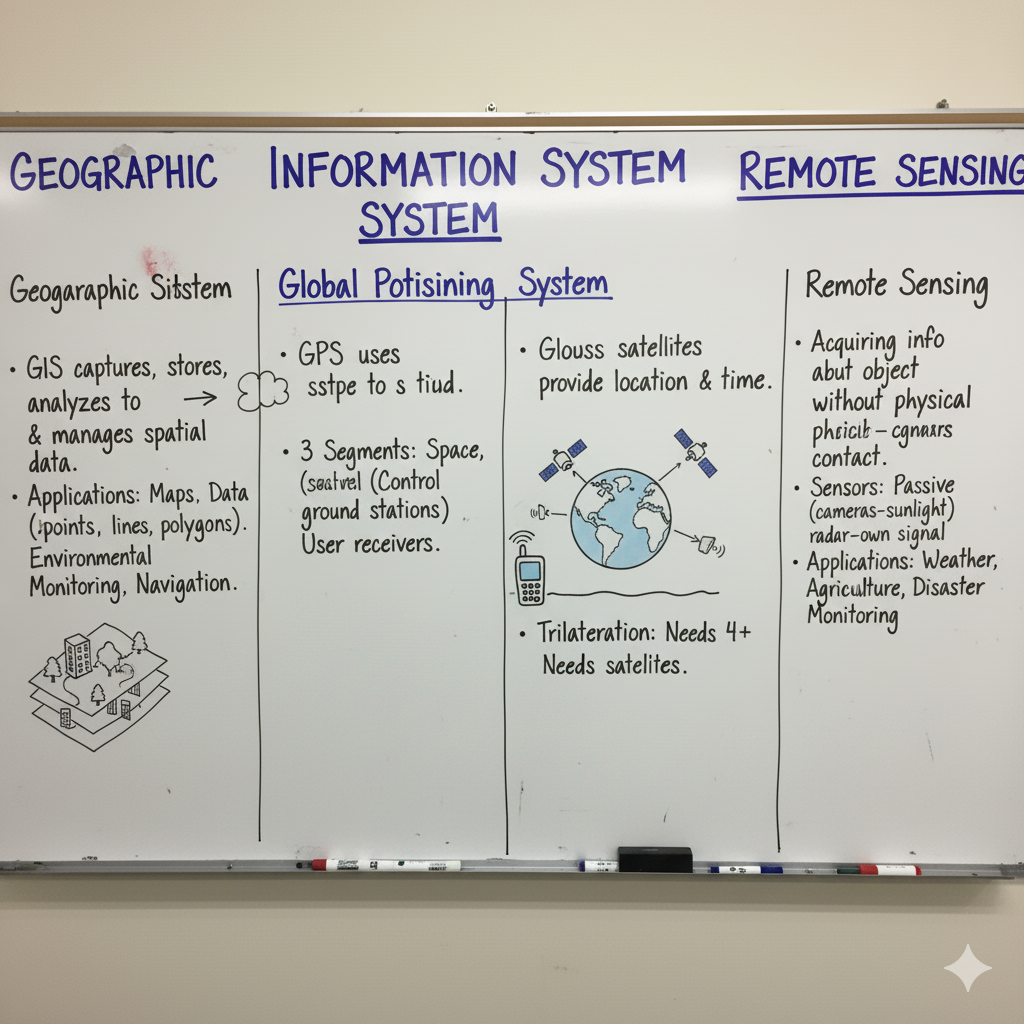
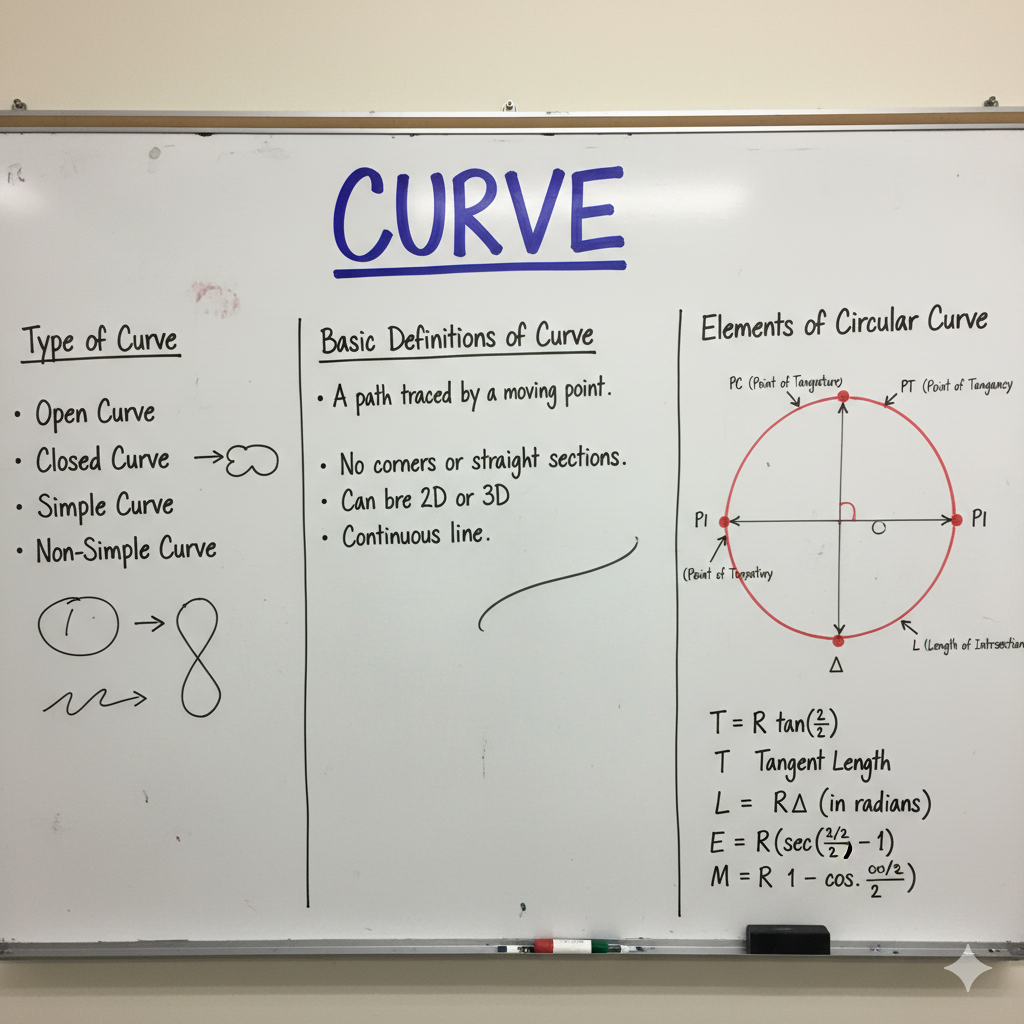
To determine the exact location and shape of natural and man-made features on the Earth’s surface.
-
To establish property lines, boundaries, and rights-of-way.
-
To determine the topography, contours, and elevations of a site.
-
To assess the soil, rock, and water conditions of a site.
-
To provide accurate data for the planning, design, and construction of infrastructure projects, such as buildings, roads, bridges, and pipelines.
-
To determine the dimensions, angles, and positions of objects for mapping and engineering purposes.
-
To study the physical and natural characteristics of the Earth’s crust.
-
To resolve land disputes and establish property ownership.
-
To provide information for resource management, such as mineral and water resources.
-
To support legal and governmental requirements, such as property taxes and land use regulations.