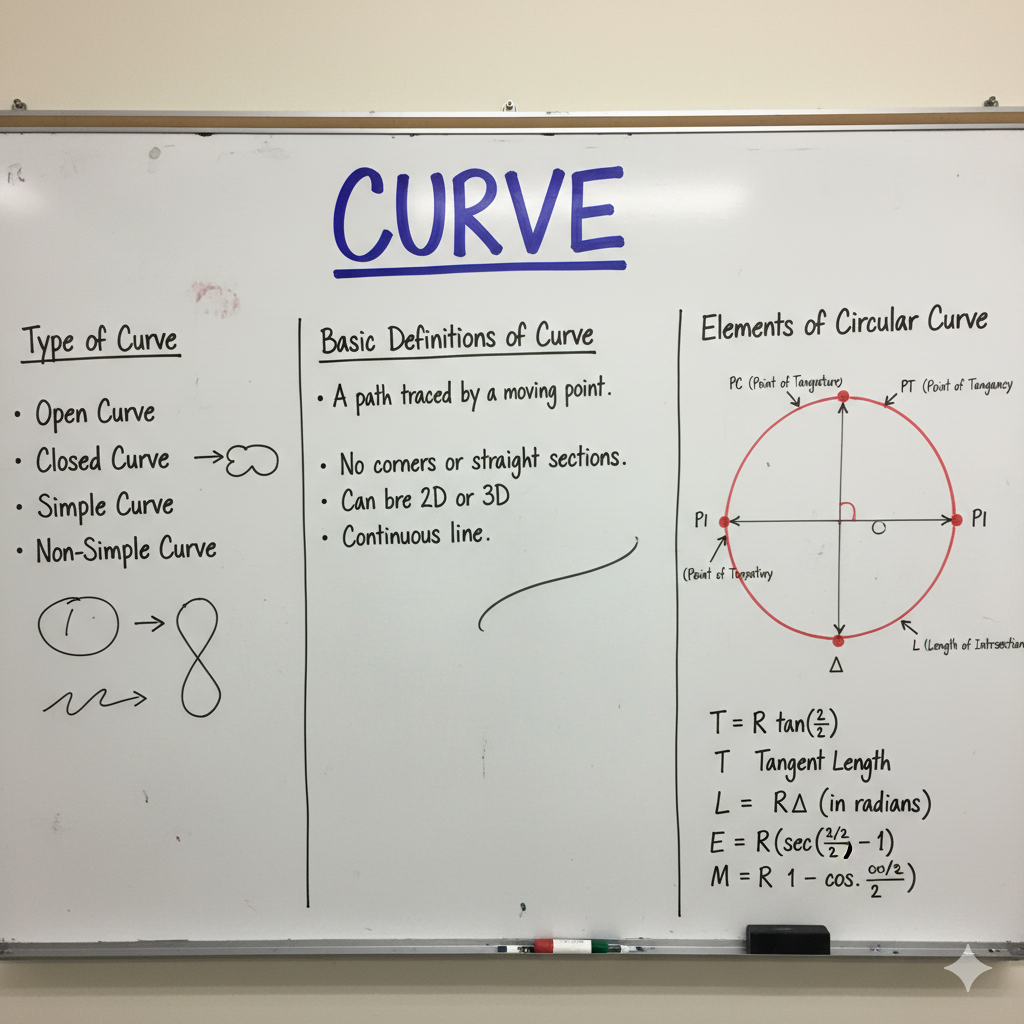
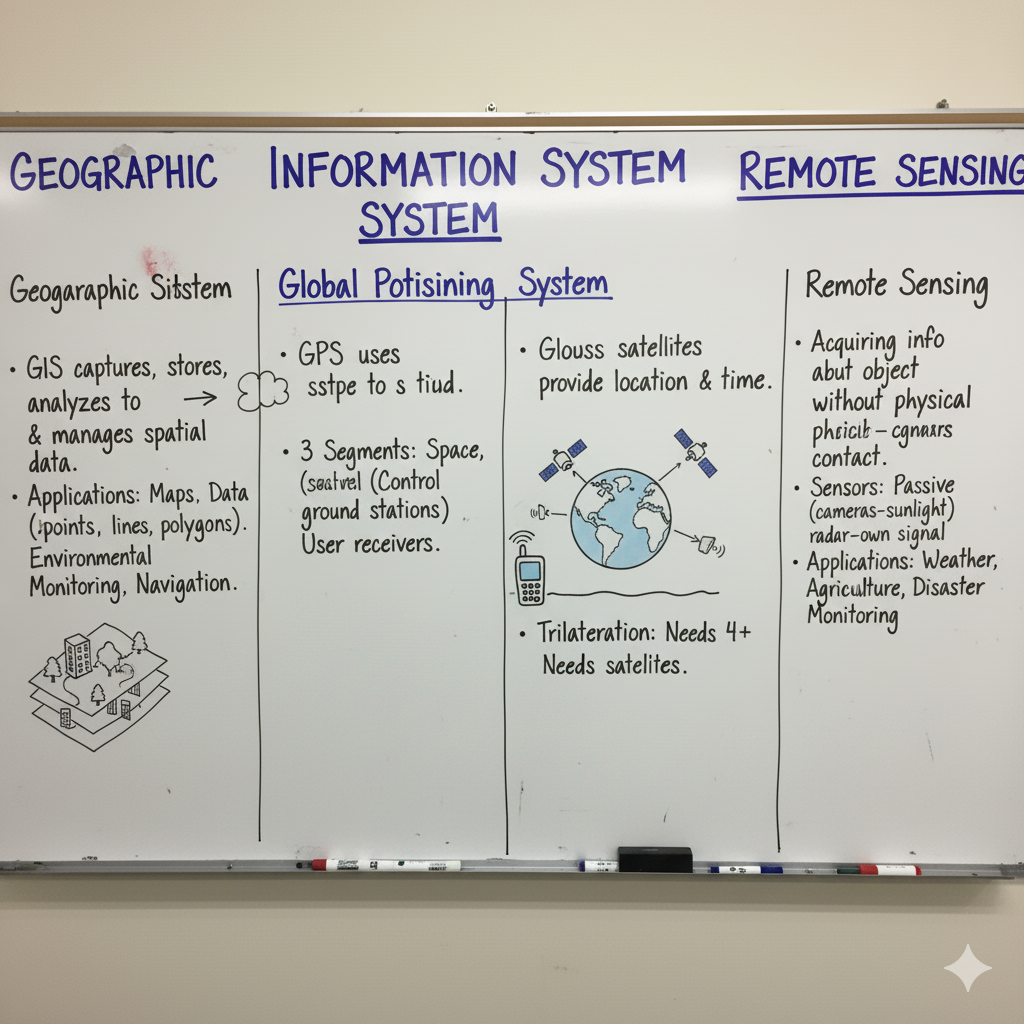
Surveying can be classified into the following categories based on the type of measurement and application:
-
Geodetic Surveying: deals with large-scale, precise measurements of the Earth’s surface, including its shape, size, and gravity field.
-
Plane Surveying: deals with smaller-scale, two-dimensional measurements of land, including the location of boundaries, topography, and features.
-
Engineering Surveying: provides critical information for the planning, design, and construction of infrastructure projects, such as buildings, bridges, roads, and utilities.
-
Mining Surveying: deals with the measurement and mapping of mines and mining operations, including shafts, tunnels, and ore deposits.
-
Hydrographic Surveying: deals with the measurement and mapping of bodies of water, including rivers, lakes, and oceans.
-
Photogrammetric Surveying: deals with the measurement and mapping of the Earth’s surface using aerial and satellite imagery.
-
Geospatial Surveying: combines the use of technology and surveying techniques to create and manage geospatial data, such as maps and digital models.
-
Construction Surveying: provides critical information for the construction and management of building and infrastructure projects, including site preparation, foundation layout, and as-built surveying.
-
Land Surveying: deals with the measurement and mapping of land and property boundaries, topography, and features, including boundary surveys, topographic surveys, and land title surveys.